Today’s Space Mining is growing Tomorrow’s World Economy and Dreams
- Team Bulls&Bears

- Feb 9, 2022
- 5 min read
BullsandBears - finance club at PDEU collaborated with Brahmand - Astronomy club at PDEU to bring together the world of finance and space.
Space mining is the collection of raw materials from their natural location, which is allowable under the Outer space Treaty. These materials can be reduced to possession, sale, trade, exploration, or scientific pursuits. The ores, stones, and even gaseous products are all found in the space mines. There are around 16,000 asteroids in the Earth’s orbit, and it holds approximately 2 trillion tones of water and many rich minerals and metals. All these materials are essential for us. The first space mining project was executed in 2016 by NASA. It involved the launch of the OSIRIS-Rex rover to the nearby asteroid Bennu, collecting the samples, and bringing them back to Earth. The total cost of the project was around 1.16 billion dollars.

It is a well-known fact that the energy resources on Earth are limited. Not to mention, there are no rules that restrict the use of these resources. Green energy contributes to 28% of total global energy. Also, the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are increasing year by year, contributing to global warming. To fight this situation, we have to mine the surface of the planets, asteroids, or celestial bodies to get the minerals, energy sources that will be useful for us in the future.
There is a possibility that these resources have the potential to provide an unlimited source of energy which we can use to eliminate the current scarcity of the same. Due to these reasons, space industries and governmental organizations started conducting Space mining projects.

The US Apollo mission was to bring back the rocks from the moon to Earth in 1969-72. The Hayabusa 2 mission, which the JAXA organized, was undertaken during 2014 and brought samples back to Earth in 2020. This mission cost around 150 million USD.

The Arkyd satellite series mined the asteroid in 2018. It was a 3-satellite series, one for finding the resource on the asteroid, one for landing the rover on the surface and mining, and one for finding resources in deep space. Many projects are undertaken for space mining on the asteroids - like Bennu, Ryugu, 1989 ML, etc. The success ratio of asteroid mining is 60%.
Space mining can also be executed on the bodies/ planets like the moon, mars, etc. We cannot perform the mining on the gaseous planets.
There are a few projects of space mining currently in progress. The OSIRIS-Rex sent by NASA in 2016 arrived at its target in 2020. It will finally return to Earth in 2023. The DART mission, an ongoing NASA asteroid redirection test, was launched in 2021.

We can mine on an asteroid surface just like we mine on Earth. Firstly, satellites find the minable areas (rich in resources) on the asteroid for mining. Then a space vehicle is launched that contains the mining machine and suitable container for samples. It reaches the targeted area and collects the resources. After extracting the mining samples in the container vessel, it returns to Earth. There are many challenges that we have to face when returning the samples. If the spacecraft gets damaged during landing, it may not successfully reach Earth. There are also difficulties in flying through the asteroid belt of the Earth. The heat generated during the re-entry of the spacecraft in Earth’s atmosphere may affect the soft samples.

In the upcoming years, The Phobos-Grunt 2 mission prepared by Roskosmos is to collect the sample from Phobos and return it to Earth in 2024. The VIPER rover, planned by NASA, is to prospect for lunar resources in 2023.
Asteroid mining provides us with unlimited sources of energy and water to meet the current demand. Asteroids and planets contain a wide range of minerals, from water vapour to gold and platinum. Mining is useful for exploration and can fulfil one's need for adventure.
Many cons of space mining are the unknown minerals returning to the Earth that can be harmful to humans if they are radioactive. The cost of spaceflight is high. Any NASA-SpaceX-Boeing orbital trip would require 58 million dollars on average, along with the additional cost of space mining equipment. The Projects targeting asteroids near Earth can have a 492 million dollar price tag. Mining on the moon can initially cost 9 million dollars.

Many private industries and governmental space agencies are in the race to mine space like NASA, Roskosmos, Deep space agency, Kepler energy and space engineering. By asteroid mining, the industries get the rich metals that cost trillions of dollars. Life on another planet is only possible when we know its atmosphere, surface, and other conditions.
Earth is essential for mankind, but space mining and interplanetary travel are essential for the future of humanity. The Hayabusa spacecraft successfully collected samples from the Itokawa asteroid in 2010. The asteroid contains olivine, pyroxene, iron sulfides, and plagioclase.
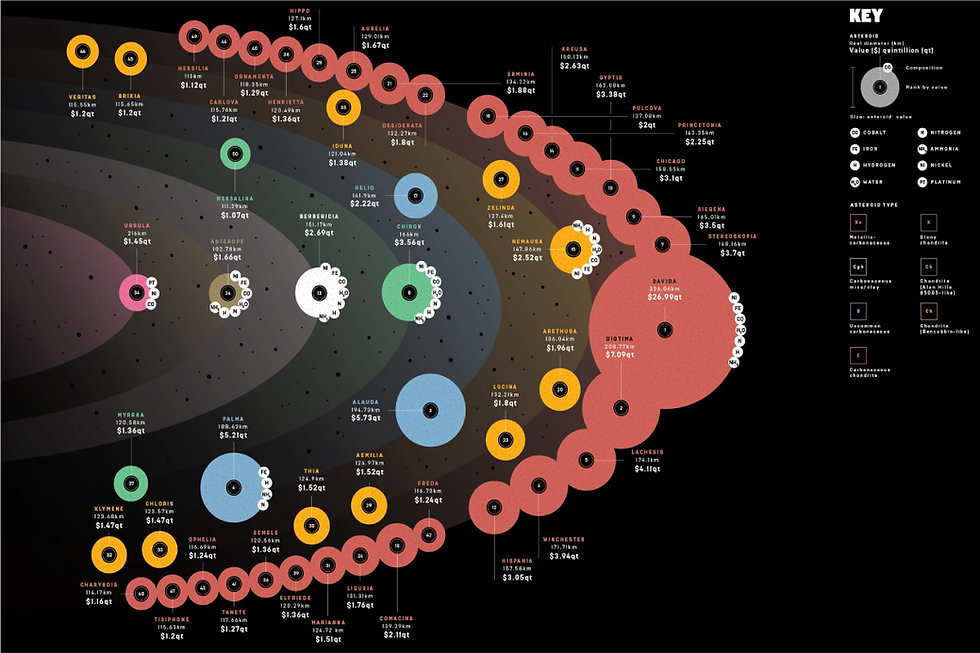

The asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter accounts for $700 quintillion worth of precious metals. If this were to be divided among the current population, each person would come out with $100 billion. It could be the future of space mining once we develop advanced robotics and AI to overcome the complications.
The US and Luxembourg might have been the first to develop plans for space mining, but many countries have now joined the race. UAE, China, Russia, India, South Korea, Germany, France, and many more are working towards this goal. Europe is the fastest-growing market for space mining, while Asia is the biggest. Currently, the space mining market value is a billion dollars. These space activities were worth around 715 million dollars in 2017. But with advanced robotics and AI, the space mining industry is forecasted to reach $3.9 billion and $7.3 by 2025, and 2035 respectively.


The asteroid mining corporation, a company based in the UK, is collecting crowdfunding for their future project named “EI Dorado”. This project analyzes the 5,000 asteroids and finds suitable and valuable asteroids for mining. The deep-space agency for mining has had a market value of 10.62 billion dollars since 2020.
NIAC is a program under NASA that aims to fund projects that find and develop aerospace concepts. Originally known as NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts, the program was remodelled in 2011. It is now known as NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts. NIAC has three different phases based on duration: Phase-1, Phase-2, and Phase-3. A total of 27.3 million dollars was spent on project funding from 1998 to 2007. Arkyd Astronautics, now known as Planetary Resources, was founded on 1 January 2009. The company’s goal is to start and grow a robotic asteroid mining industry. In 2016, the company acquired 21.1 million dollars through funding and an additional 25 million investment from Luxembourg. But it later faced funding issues in 2018, due to which its first space mission got delayed indefinitely.
If we find a planet capable of sustaining human life, then it will be a breakthrough in the history of mankind. For the future of humanity, space mining is the answer to our resource problem. Advancements in space technology are supporting and increasing the prospects of space mining. Consumer demand for energy will see a threefold increase by the middle of the 21st century. Space mining just might be the solution to this problem.

Written and edited by: Megha Mistry (Team BullsandBears)
Jenish Hapalia (Team Brahmand)
Photo Credits:
Figure 1. OSIRIS-Rex. Source: Los Angelas Times
Figure 2. US Apollo mission. Source: Space
Figure 3. Arkyd mining mission. Source: SciTechDaily
Figure 4. DART mission. Source: Financial Express
Figure 5. VIPER mission. Source: N.A.S.A.A
Figure 6. Asteroid Mining Meme. Source: Chamberlain, J. (2017)
Figure 7. Valuable raw materials orbiting in the Mars-Jupiter Asteroid belt. Source: WIRED
Figure 8. Most valuable asteroids in the belt. Source: https://images.app.goo.gl/k3i5UGvvJqtkpjh1A Figure 9. The growth rate of the space mining belt (2021-2035). Source: Mordor Intelligence
Figure 10. Opal Mining. Source: Cloud Front Net
Figure 11: Asteroid Mining. Source: https://images.app.goo.gl/Jj3FgJuyWMbFeEZr8




Comments